What Does Zinc Plating Mean?

Zinc plating, also known as zinc electroplating, is an electrochemical technique that deposits zinc ions onto the surface of a metal object by applying an electric current.
The major goal of this coating is to provide a protective barrier that decreases the metal’s exposure to moisture and oxygen, both of which contribute to rust development. By functioning as a sacrificial anode, the zinc layer corrodes preferentially, maintaining the integrity of the metal beneath.
What Are The Different Types of Zinc Plating?
Zinc plating includes a variety of processes and finishes used to improve the corrosion resistance of metal components.
Yellow Zinc Plating
This kind is commonly used in the automobile sector and provides moderate corrosion protection. It is distinguished by its brilliant yellow hue, which is obtained by a chromate conversion process.
Blue or Clear Zinc Plating

This finish, which is commonly used for machine components, screws, and washers, has a shining look and is popular due to its aesthetic advantages. It has strong corrosion resistance, but is less protective than yellow zinc.
Black Zinc Plating
This kind produces a dark finish, ranging from olive drab to complete black. It is commonly applied for ornamental purposes and provides improved rust resistance, especially when paired with black oxide treatments.
Acid Zinc Plating
Acid zinc plating, used for difficult-to-plate surfaces, employs an acidic electrolyte solution to provide quicker deposition rates and greater coverage of complicated geometries. Its efficiency makes it ideal for high-volume production.
Zinc-Nickel Plating
This version adds nickel into the zinc coating, resulting in higher corrosion resistance than ordinary zinc plating. It is very helpful in harsh conditions, such as automotive applications.
Zinc-Iron Plating
This approach mixes zinc and iron to increase corrosion prevention and wear resistance. It is commonly utilized in situations that require greater strength.
Barrel Plating
A method in which tiny items are put in a spinning barrel containing zinc plating solution to provide equal coating on all surfaces.
Rack Plating
Larger objects are put on racks and immersed in the plating solution, providing fine control over the plating process.
Zinc Plating Equipment and Materials
Zinc plating equipment and supplies are critical components in the zinc plating process, which includes depositing a thin coating of zinc to metal substrates to prevent corrosion. Here’s an overview of the various equipment and materials used in zinc plating.
Zinc Plating Equipment
Plating Tanks
Tank Plating: A huge tank filled with zinc plating solution into which items are submerged for plating.
Barrel plating: it is a spinning barrel that contains smaller pieces, providing consistent covering as it revolves.
Power Supply
A direct current (DC) power source is required to power the electroplating process by supplying the appropriate voltage and current to assist the migration of zinc ions from the anode to the cathode (the plated component).
Anodes
Zinc anodes are used in plating baths to provide zinc ions. These anodes progressively disintegrate throughout the plating process, ensuring a steady supply of zinc.
Heating Equipment
Heating elements may be required in some procedures to maintain ideal temperatures for the plating solution, hence improving the deposition rate and coating quality.
Filtration Systems
Filtration systems aid in the purity of the plating solution by eliminating contaminants and particles that might degrade the zinc coating.
Rinsing Stations
After plating, the pieces are washed with water to remove any remaining chemicals from the surface, avoiding contamination and assuring a clean finish.
Zinc Plating Materials
Plating Solution
Zinc salts (such as zinc sulfate or zinc chloride) are commonly used in electrolyte solutions, along with additional additives to improve plating properties like as brightness and corrosion resistance.
Cleaning Agents
Before plating, items must be cleaned using alkaline cleansers or acids to remove oil, grime, and oxides from their surfaces. This step is critical for ensuring effective adherence of the zinc layer.
Passivation Agents
After plating, passivation treatments can be used to increase corrosion resistance and change the look of the zinc coating. Common treatments include chromate conversion coatings, which can impart a variety of hues (for example, yellow or iridescent).
Safety Equipment
Personal protection equipment (PPE), such as gloves and goggles, are required for safety when handling chemicals and operating plating equipment.
Waste Management Solutions
Environmental rules need proper disposal solutions for hazardous material created during the plating process.
The Step-By-Step Zinc Plating Process
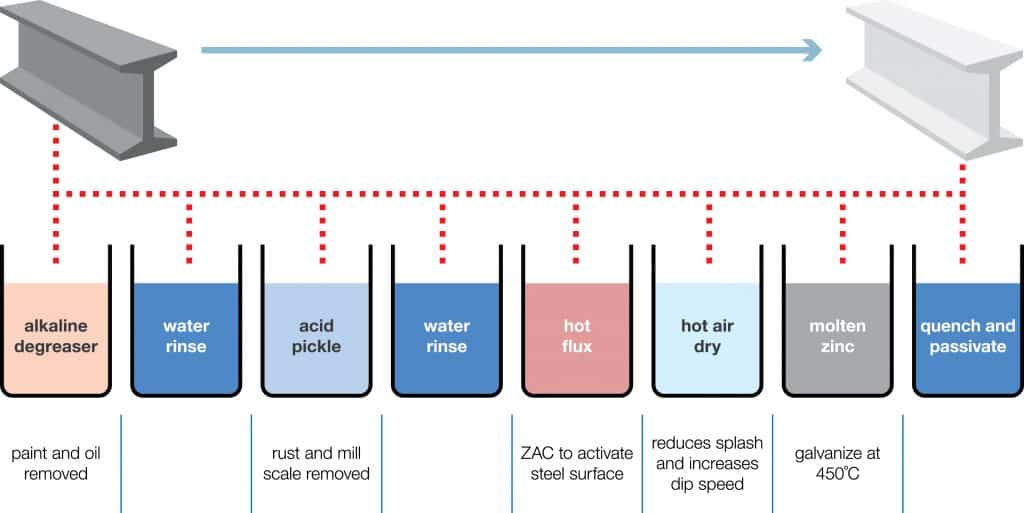
The zinc plating process is a systematic method used to apply a protective zinc coating to metal surfaces, enhancing their resistance to corrosion. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide to the zinc plating process:
Step 1: Surface Cleaning
Before plating, the metal substrate must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants such as grease, oil, and dirt. This is typically done using:
- Alkaline Detergent Bath: The metal is soaked in a hot alkaline solution (around 150°F) for 5-10 minutes to eliminate surface impurities.
- Electrocleaning: An electric charge is applied to the metal, which helps to clean the surface at a microscopic level by releasing gases that lift contaminants away.
Step 2: Pickling (Activation)
After cleaning, the substrate undergoes a pickling process to remove any oxides or scales that may have formed. This involves:
- Acid Treatment: The metal is submerged in an acidic solution, often containing sulfuric or hydrochloric acid, which helps to prepare the surface for plating by ensuring it is clean and reactive.
Step 3: Preparation of the Plating Bath
The plating bath is crucial for the electroplating process. It typically consists of:
- Electrolyte Solution: A solution composed of water, zinc salts (such as zinc sulfate or zinc chloride), and different additions to improve plating quality. The solution must be properly produced in order to get the necessary chemical and physical characteristics of the zinc coating.
Step 4: Zinc Electroplating
Once the substrate is prepared and the plating bath is ready, the actual plating process begins:
- Submersion: The cleaned and activated metal is immersed in the plating bath.
- Electrical Current Application: A direct current (DC) is applied, causing zinc ions from the anode (zinc source) to deposit onto the substrate (cathode). This step can be performed using either rack plating (for larger parts) or barrel plating (for smaller parts) to ensure an even coating.
Step 5: Post-Electroplating Treatment
After the plating process, the coated parts may undergo additional treatments to enhance their properties:
- Rinsing: The plated items are rinsed to remove any residual plating solution.
- Drying: Proper drying techniques are employed to prevent oxidation of the newly plated surface.
- Optional Coatings: Additional protective coatings, such as chromate conversion coatings, may be applied to further enhance corrosion resistance and improve appearance.
The Benefits of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating has multiple benefits, making it a popular choice for safeguarding metal components in a variety of sectors.
Corrosion Resistance
Zinc plating acts as a sacrificial anode, providing high corrosion resistance. This implies that zinc corrodes before the underlying metal, significantly extending the life of steel or iron products. Zinc has a far lower corrosion rate than ferrous materials, making it a dependable barrier against rust and oxidation in a wide range of situations.
Cost-Effectiveness
Zinc is a plentiful and affordable substance, making zinc plating a cost-effective alternative to conventional metal finishing methods. Lower material prices, along with reduced energy use during the plating process, result in total savings for producers.
Thin Coating
The zinc coating deposited by plating is generally thin (approximately 8-12 microns), which is useful for tiny and delicate components. This thin coating has no substantial effect on part dimensions, making it suitable for precision technical applications.
Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal
Zinc plating may enhance the visual look of metal objects, with finishes ranging from bright and lustrous to matte or colored alternatives (such as yellow or black). This adaptability enables producers to create desired looks while also benefiting from protective properties.
Compatibility with Other Coatings
Zinc plating is a good undercoat for other finishes like paint or powder coating. Zinc’s high adhesive qualities improve the bonding of following layers, resulting in increased overall durability and attractiveness.
Electrical Conductivity
Zinc is an excellent conductor of electricity, making zinc-plated components appropriate for use in electronics and telecommunications. The coating enhances solderability and guarantees dependable electrical connections in devices such as connectors and circuit boards.
Versatility
Zinc plating is widely used in a variety of sectors, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and general manufacturing. Its ability to cover a wide range of metal components, from fasteners to structural pieces, making it an excellent solution for a variety of applications.
Reduced Maintenance
Zinc plating eliminates the need for regular metal part maintenance and replacement due to its strong corrosion resistance. This results in cheaper long-term expenses and higher service dependability.
What are the common applications of zinc plating?

Automotive Industry
Zinc plating is often utilized on automobile parts such as nuts, bolts, brackets, and fasteners. It protects these components from rust and wear, increasing their longevity and performance. Additionally, car body pieces such as frames and panels are frequently zinc-plated to protect them from harsh weather conditions and road salt exposure.
Construction and Infrastructure
Zinc plating is used in construction to prevent corrosion on steel beams, pipelines, and fittings. This is especially true for constructions exposed to the weather, such as bridges and buildings. Zinc-plated rebar is also utilized in concrete to improve the lifetime of the foundation.
Military Applications
Zinc plating is essential for military-grade applications where components must survive extreme conditions. It is used on components of tanks, armored personnel carriers, and other military vehicles to improve their corrosion resistance and endurance.
Consumer Electronics
Small consumer electronics components, such as connectors and switches, are frequently zinc-plated to increase durability and corrosion resistance. Zinc plating has an aesthetic appeal that makes it suited for visible portions in electronic equipment.
Industrial Equipment
Zinc plating is commonly used in industrial applications for components such as machinery parts, tools, and equipment that require increased durability against wear and tear. This comprises fasteners that are utilized in heavy machinery and construction equipment.
Household Appliances
Zinc plating is often used to preserve metal parts in home appliances against rust while also improving their look. This consists of hinges, brackets, and other hardware components.
Aerospace Components
Zinc plating is utilized on different aircraft components that must be corrosion resistant while preserving structural integrity under high-stress circumstances.
Conclusion
Zinc plating is an important procedure for improving metal durability and corrosion resistance. Its many coatings, ranging from drab gray to lustrous, have both functional and aesthetic value. Zinc plating is widely used in automotive, construction, and electronics, and it provides lifespan and performance, making it an excellent choice for safeguarding metal surfaces.